Become an ExO
EXO!
WHAT IS IT?
WHAT DO EXOs DO?
CAN I DO IT?
Translation: SkyViewCRM e-book No. 18, copyright SkyViewCRM
YOUR CHALLENGE
How does your company become an ExO?
THE PROBLEM
ExO means Exponential Organization – a term launched by Salim Ismael in 2014, in his bestseller “Exponential Organizations”. They are called so because they grow exponentially as opposed to linearly, as traditional companies do. Examples: AirBnB, GitHub, Local Motors, Quirky, Google Ventures, Uber, Tesla, TechDept, Build Direct, Coyote Logistics. Twenty years ago, it took more than 20 years for a company to be worth a billion US$ – a Unicorn. Now it takes an ExO a few months. Within the last four years, the number of Unicorns has increased from 39 to 223. The subtitle of Salim Ismael´s book reads:
Why new organizations are ten times better, faster, and cheaper than yours (and what to do about it).
That’s what you can find out by reading the present e-book. It is a current topic that is highly relevant to more than half of all small and medium-sized businesses – SMEs. Yours too, maybe. Not only because most SMEs do not grow but also because they become “disrupted” – closed down – if they do not change radically. You can read about disruption in our e-books No.s 15 and 17.
Exponential growth or Double Dip for SMEs?
HOW CAN YOU MEET THE CHALLENGE?
ExOs grow exponentially by means of revolutionary new business practices which build on the rapid development of multiple technologies. In our e-book No. 15 you can read about the 12+ technologies which develop very quickly. ExOs and new technologies disrupt ordinary companies, entire industries and public sectors – and jobs. The most dramatic disruption occurs from combinations of physical and digital systems. 8-9 years ago, the sensors in Google’s autonomous car cost more than 200,000 US$. Car manufacturers called the project “a nice way to lose time and money”. 2-3 years later, the cost was reduced to half. Then it was halved again. Car manufacturers were still smiling. Now the sensors cost 1,000 US$, and Google still expects major improvements. The car manufacturers smile no more. [Quote: Samuel Ismael at a webinar].
Some of the largest companies (and even geographical regions like Medellin in Colombia) has now begun using the ExO methods, assisted by ExO experts.
An example is the Tesla car – an app on wheels. The cars´ performance is remotely updated and improved through its software. Thus, Tesla Motors is not a car manufacturer. Neither is Uber a transport company (as the EU Court of Justice recently defined it).
SMEs
99% of all Danish companies are SMEs. Yours too, probably, and then it is much better equipped to grow exponentially than the largest companies. SMEs:
- are more flexible
- have a built-in ability to change quickly
- have a deep knowledge of their products, services and customers
Still, only a few of the SMEs are growing at all. Generally, it is because SMEs:
- are only represented in one or a few countries
- focus on their existing products / services and customers
- do not aim at growing and generating cash for development
- have limited interest in – and ability to – attract investment
SMEs are highly dependent on their boss / owner who is often busy with day-to-day solutions and maintaining a high efficiency. They often have a limited network, not much access to knowledge about global trends and events, or to exchange ideas about expansion. They are not aware of new business models that are going to completely change the rules of the game within the next 2-5 years. During that period, however, only a minority of them plans to invest in new technology or digitization. Thus, SMEs constitute a major threat to our prosperity and well-being – a threat that receives limited attention and action from politicians, employers´ and workers’ organizations. For the thousands of SME owners who are faced with generational change it will be a sudden awakening to realize that their firm may be worthless.
The latent growth potential of SMEs can only be exploited if the owners / managers will – and will be able to – use new technologies and create radically new business models.
METHODS
Turn your business into an ExO. Not tomorrow. Not “when I find the time”.
NOW!
ExOs use completely different business models and methods using the latest technologies – especially digitalization. You can also use these models and methods and thus end up among the winners.
BECOME AN EXO!
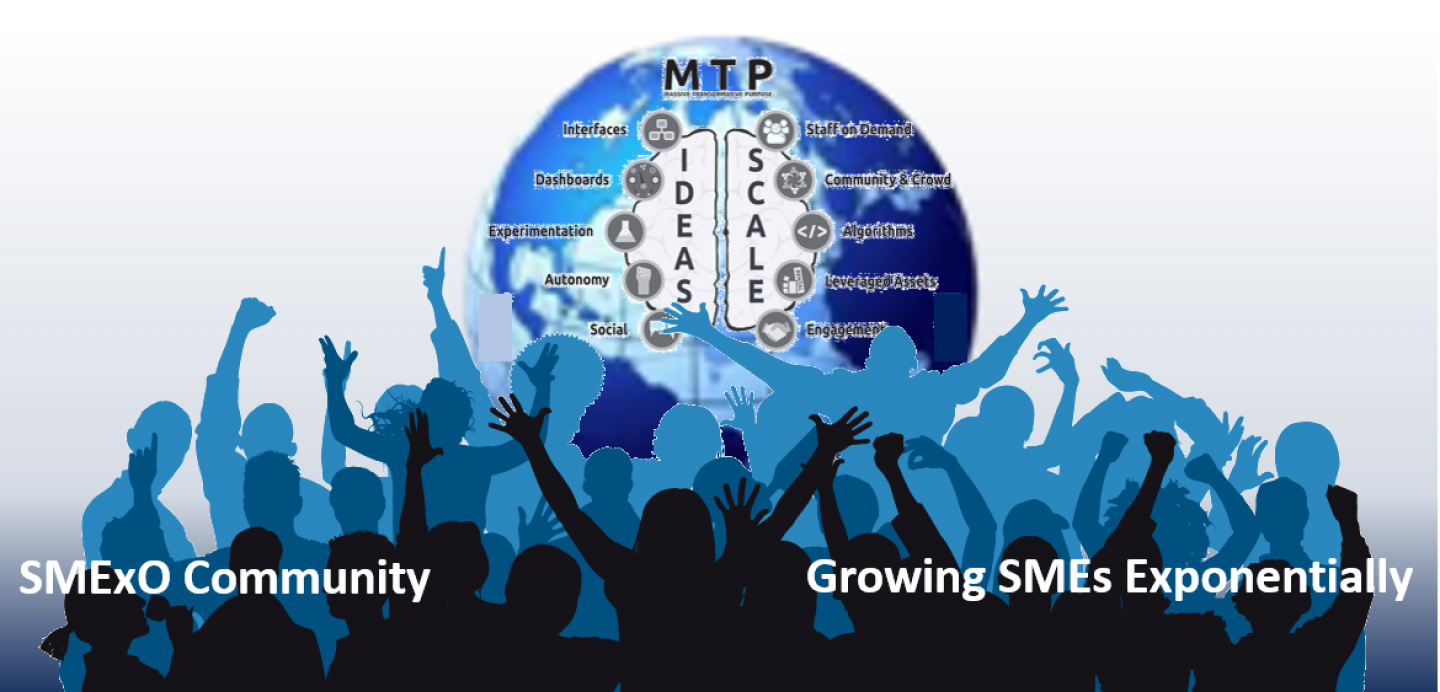
Here is an overview of the eleven ExO methods:
- MTP, which is an abbreviation of “Massive Transformative Purpose”
- S.C.A.L.E. – abbreviations for 5 externally focused methods
- I.D.E.A.S. – abbreviations for 5 internally focused methods
All ExOs have an MTP, but they do not necessarily use all the other ten methods. They may start with 4-5 of them and then gradually use some of the others.
MTP – WHAT IS IT?
It is a purpose that will lead to radical change. Many companies have formulated their purpose in the form of a “Mission” – a description of what the company does. MTP differs from that by:
- denoting a strong will to radically benefit the world
- being based on an external problem or condition rather than on the functions of the company
An MTP enables everyone to think on a grand scale – and to use their skills on fulfilling the purpose.
Requirements for the MTP:
- It must comply with all three words (Massive Transformative Purpose)
- It must describe a clear “why”. Why do you do that? Why is it revolutionary?
- It must be unique and difficult to copy
- It must be wildly ambitious. Must create passion and a common sense of meaning among the stakeholders of the company
- It must require constant action by all involved
- It must focus on radical change on a large scale (for millions of people, communities, industries —). On solving a big problem for a lot of people
Take care, energy and time together to reach a short, sharp, clear wording, which everyone – and especially you, your collaborators and audience – immediately understands and feels highly attracted to. Your ExO future depends on it!
S.C.A.L.E – Externally Focused Methods
S – Staff for Hire
Instead of hiring people, you find and use freelancers with top competencies on the internet.
C – Community & Crowd
You create a community on the internet where everyone with a passion for your MTP meets. Here, you can use their help and skills in creating a unique solution. You also use the Internet to get creative input and evaluate your solution, and to get funding (“Crowd Funding”).
A – Algorithms
– is a very powerful, computer-based tool that is already widely used to create order and meaning in data. With that you can significantly increase efficiency and process speed, and reduce costs.
L – Lease or share assets,
– instead of owning them. This minimizes the need for capital and increases your freedom of movement.
E – Engagement
You involve your employees, customers and others in creating value. Using MTP, openness, delegation of powers, competitions, games, etc.
I.D.E.A.S – Internally Focused Methods
I – Interfaces
– are automated processes and algorithms that you use to filter output from external contacts such as Staff for Hire and Communities, for internal functions.
D – Dashboards
Digital bulletin boards that you use to present real-time data, goals and key results (KPIs), thus motivating your employees (and yourself), creating focus and energy, and a positive culture.
E – Experimental
You drop traditional linear planning and development procedures. Instead, you experiment and use process iteration to match your new products and services with customer wishes and needs, and evaluate bottom-up ideas. Techniques like “Lean Startup” and “Minimum Viable Product” make your development much safer, cheaper and faster, reducing risks and capital requirements.
A – Autonomy
You give your competent and talented employees great freedom to participate in business development and to launch innovative projects on their own. This results in greater flexibility, faster response and learning, high work ethics and commitment.
S – Social technologies. Use them to:
– reduce the distance between receipt and processing of information and decision
– switch from searching information to receiving a flow of information
– develop ideas in cooperation with your community
HOW TO CHOOSE AMONG THE EXO METHODS
Here you can measure how ready your business is for exponential growth and see which methods to use:
ExO Canvas is a supplementary tool that you can use to use select methods and develop your business:
DETAILS OF A COUPLE OF THE METHODS
It is beyond the scope of this e-book to go into detail with the 11 ExO methods but in the following sections we give you a deeper insight into two of the methods: MTP, and Staff for Hire.
MTP
MTP is the very basis of any ExO business. It enables users to “think big” – to use the skills of the organization to radically change an industry, or to create massive improvements in an important field of human life. It unites and motivates the company’s internal and (present and future) external actors to engage in improving life for numerous people. It opens up for market opportunities which are many times larger than otherwise imagined.
An MTP is the prerequisite for effective use of six out of the 10 ExO methods, namely: Staff for Hire, Community & Crowd, Engagement, Experimental, Autonomy, and Social Technologies.
Some examples of an MTP
Singularity University: Building an Abundant Future Together
Google: Organize the World’s Information
SMExO IVS: Growing SMEs Exponentially
ProductionScale Inc.: To Apply Technology for Humanity
How do you create it?
You start from the outside – in your business environment. Use your knowledge of customers, or of any other group of people. Expand your knowledge to similar groups – regionally, internationally, and globally. Complement your knowledge by retrieving information from as many sources as possible. Think carefully about problems, needs, attitudes, settings and behaviors of groups of people which could open up for dramatic improvements. Just like Facebook, Google and other ExOs do. Think: if you can imagine it, it may be possible – just like Elon Musk thought about an app that became a “car” – Tesla.
Then proceed on the basis of how to “disrupt” your business before others do. What quite different business models will make your business and industry redundant? Do not deny that it will happen – because it will – for the majority of all existing companies (and jobs).
Consider your ideas in the light of the competencies you have access to in your business and those you can find through your current and future network. Include existing and soon emerging opportunities for exploiting technological achievements. Keep in mind that almost “everything” can or will be digitized and moved to the Internet.
Discuss all of it with clever and experienced as well as untraditional and imaginative people – in your company and in your network.
STAFF FOR HIRE
The vast majority of SMEs cannot attract or pay top experts with crucial, value-creating skills. And no matter how talented your employees are, most of them will gradually become less competitive or lack the skills your business needs to survive. Previously, the half-life of an acquired skill was around thirty years. Now it’s about 5 years and steadily declining.
Thanks to the Internet, it has become easy and almost free to find external employees, and the number and quality of freelancers has risen dramatically.
Why do SMEs demand external skills and competencies?
The increased presence of digital technology and artificial intelligence leads to new job functions and
categories, but also to lack of people with the necessary skills to fill in the roles. Automation replaces jobs, and “Big Data” as well as advanced analytics tools allow deep insight into customers, management and employees. Enhanced access to information and ideas blurs the limits of what is inside and outside the company.
Digitalization of products and services creates a huge demand for talented digital skills. Nearly half of US and German companies in a Boston Consulting Group survey indicated the lack of qualified employees as the main obstacle to complete digital conversion. Companies are forced to develop or gain access to talent in growing specialties such as data analytics, app development and user experience design. Almost any job will eventually require the use of sophisticated technology.
Knowledge-intensive companies are increasingly outsourcing work. Partly to save costs and partly to save their best employees for work that creates the most value. More and more knowledge and routine work is being given to individual external persons instead of, as before, to subcontractors.
Staff on Demand offers most of the functionalities and benefits that SMEs can use: no need for office space, no permanent employees, smart computing to connect people’s needs with others’ tasks, online meetings, global access to time and knowledge.
This speaks for using Staff on Demand
Staff on Demand gives SMEs access to specialists with up-to-date knowledge in many areas,
and the cost is 100% variable.
This speaks against using Staff on Demand
Staff on Demand knowledge may not be fully rooted in the company. Community feel and team building are hampered by external employees from other cultures and time zones, and physically separate from the company.
These are the challenges of using Staff on Demand
- How to find, select, and measure the value of external employees?
- How to communicate when internal and external employees do not speak the same (business) language?
- How to maintain the changes caused by cooperation with external employees when cooperation ceases?
Why is there increasing access to external skills and competencies for SMEs?
New settings among skilled people change working methods – especially the increasing preference for independent work rather than a career in a large organization. Independence is becoming the dominant motivational factor for many people, especially for millennials (born early in the 1980s to mid-1990s), and Gen-Zere (born in the mid-late 1990s and beyond). These younger people feel bored when they have to do the same things for a long time, and they are most interested in independent careers. Digital platforms and online ecosystems allow them to choose entrepreneurship and self-employment rather than employment in large companies. Working in and being paid in multiple projects is especially interesting for talented people.
How can you access these skills and competencies?
The opportunity to get information and ideas from anywhere and everywhere in the world increases exponentially. People can be continuously connected, use data from anywhere, work easily with remote access, and collaborate with global colleagues in real time. Companies do not even need employees: In many leading IT companies, external suppliers make up almost half of full-time workers.
Fast expanding internet access allows for crowdsourcing and sub-economics. The most innovative solutions are now being developed by people all over the world, joining in online communities, on internet platforms, and digital ecosystems. They also disrupt traditional models for venture financing, product development and product life cycle management.
Crowdsourcing communities like Kaggle and Incentive allow companies to hire talents almost without prepayment. Instead of hiring full-time employees, companies can staff projects with the specific expertise they need. Freelancers bring the added benefit that they are well acquainted with development trends within their specialties – unlike permanent employees who have an unchanged, more limited network.
Topcoder can underbid its competitors by 75% by dividing projects into small bids and offering them to its 300,000 freelance developers in 200 countries, in a series of competition challenges.
InCloudCounsel underbids major law firms by up to 80% thanks to a host of freelancers who produce legal documents (such as license agreements, accreditations and secrecy agreements) for a fixed amount.
The most striking example of a Staff on Demand service is Amazon’s Mechanical Turk, where customers can post any “human intelligence task”, from drawing attention to offensive content on websites to formulating mails. Users of the site choose what they want done, depending on task and price.
Some other examples of Staff on Demand platforms are:
- Coople which focuses primarily on hotels & restaurants, events & promotion, retail, logistics, health, and business and administrative services (office work)
- Invido, a Danish platform that matches students and SME projects
- Remote: software development, design, marketing, customer support and other non-tech jobs
- Peopleperhour: Staff-On-Demand in hundreds of different areas
- Upwork: Programmers, Designers, Copywriters, Customer Support, and more.
HOW SHOULD YOU ORGANIZE YOUR COMPANY?
Managers must adapt their leadership style to the individualized culture, find new ways to inspire, and provide extended powers to individuals and teams in their looser organization.
A Management Revolution:
| BEFORE | NOW |
| The outside world is local, regional, predictable, transparent, linear | The outside world is global and complex. Radical, exponential changes |
| Market value is equal to material assets | Market value is equal to intangible assets |
| Value creation based on the professional competence of the boss. Top-down | Value creation depends on the competences, commitment and cooperation of everyone |
| Knowledge and power with the boss | Knowledge (and power) of all |
| The employees “do what the boss says” | The employees “use their own heads” |
| The manager’s tasks: planning, direction,coordination, control | The manager’s tasks: to find and maintain the best talents. Delegate wide powers. Engage, inspire, motivate, support. One-to-one management |
| Systems, structures, rules. Do as we usually do. Zero errors | Quick response, flexibility. Change, innovate, experiment, learn from mistakes |
| Inside-out | Outside-in |
Staff on Demand will revolutionize the way work is being carried out in businesses – new ways to organize, implement and lead, and new ways of recruiting, developing and motivating employees. As companies start to hire talents, they must be content with a lower degree of commitment. They must create career paths and roles that meet entrepreneurial ambitions with the highly developed talent they seek.
Companies develop a more fluid perception of what is inside and outside their borders. They go away from rigid distinctions between employees, suppliers and customers, and develop online platforms to promote collaboration between all stakeholders. Gradually, the value chain changes to networks and platforms, and the organization’s role changes from controlling resources to facilitating digital ecosystems and becoming a tool for realizing individual ambitions.
Startups use Staff on Demand as an integral part of their work. Very large companies have HR staff who can investigate and evaluate the many new Staff on Demand opportunities. SMEs have limited resources for these tasks, so how do SMEs organize themselves?
- Establish a professional board where one or more members can help bridge your operational / practical oriented culture and the academic / technical background of Staff on Demand
- Discuss HR and Staff on Demand as strategic tools on all board meetings
- Determine the crucial, value-creating skills needed to develop your business
- Create well-defined projects with clear goals and follow-up (Dashboards) to be able to describe and outsource tasks to top specialists
- Establish integration routines that support the use of Staff on Demand
- Be keenly aware of your company’s HR image. Follow it through “Glassdoor” (a “TripAdvisor” / “Trustpilot” targetting companies, with input from (former) employees)
HOW DO I GET TO KNOW MORE ABOUT EXO METHODS?
Read more on this website:
Here, you can sign up as a member of an ExO Community and receive news and information, and participate in discussions with ExO experts.
If you have not yet digitized your customer management & sales processes – or have tried in vain to find the time to do it – click here:
We help you to ensure that your customer acquisition and customer care is on the right track when you digitize the rest of your company by means of ExO methods.